Python API Documentation using Flask and Swagger
What is Swagger?Permalink
Swagger is a Specification for visualizing Restful Web Services. It represents the RESTFUL API and can be integrated with almost any programming lanugage. With OpenAPI’s specification, User can understand and consume services without knowledge of server implementation or access to the server code
In this post we will see how to built an API documentation using swagger and Flask-RESTful. Let’s get started.
A Flask-RESTful APPPermalink
We will first create a Flask rest service using Flask-RESTful which is a REST framework for creating API’s. This simple test app has a GET method which takes two numbers a and b as parameters and compute the Sum, Product and Division of the numbers
import json,os
import logging
import sys
import config
import requests
from flask import Flask, request, Response, jsonify
from flask_restful import Api, Resource, reqparse
from flasgger import Swagger, swag_from
# Setup Flask Server
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config.from_object(config.Config)
api = Api(app)
class Testapp(Resource):
def get(self):
a = int(request.args.get("a"))
b = int(request.args.get("b"))
numsum = a+b
prod = a*b
div = a/b
return jsonify({
"sum": numsum,
"product": prod,
"division": div
})
## Api resource routing
api.add_resource(Todo, '/stats')
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(debug=True)
This code looks good and everything work as expected but what is missing here is the API documentation. How can you publish and exhibit this API to the rest of the world to interact with
What is Flasgger?Permalink
We will implement API Documentation of this GET Method using flasgger which is a Flask extension to generate and built the OpenAPI specification
Flasgger also provides validation of the incoming data, using the same specification it can validates if the data received as as a POST, PUT, PATCH is valid against the schema defined using YAML, Python dictionaries
Using docstrings as specificationPermalink
We will use docstring to generate the specification for GET method of Todo Class
import json,os
import logging
import sys
import config
import requests
from flask import Flask, request, Response, jsonify
from flask_restful import Api, Resource, reqparse
from flasgger import Swagger, swag_from
# Setup Flask Server
app = Flask(__name__)
class Todo(Resource):
# @swag_from("stats.yml")
def get(self):
"""
post endpoint
---
tags:
- Flast Restful APIs
parameters:
- name: a
in: query
type: integer
required: true
description: first number
- name: b
in: query
type: integer
required: true
description: second number
responses:
500:
description: Error The number is not integer!
200:
description: Number statistics
schema:
id: stats
properties:
sum:
type: integer
description: The sum of number
product:
type: integer
description: The sum of number
division:
type: integer
description: The sum of number
"""
a = int(request.args.get("a"))
b = int(request.args.get("b"))
numsum = a+b
prod = a*b
div = a/b
return jsonify({
"sum": numsum,
"product": prod,
"division": div
})
## Api resource routing
api.add_resource(Todo, '/stats')
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(debug=True)
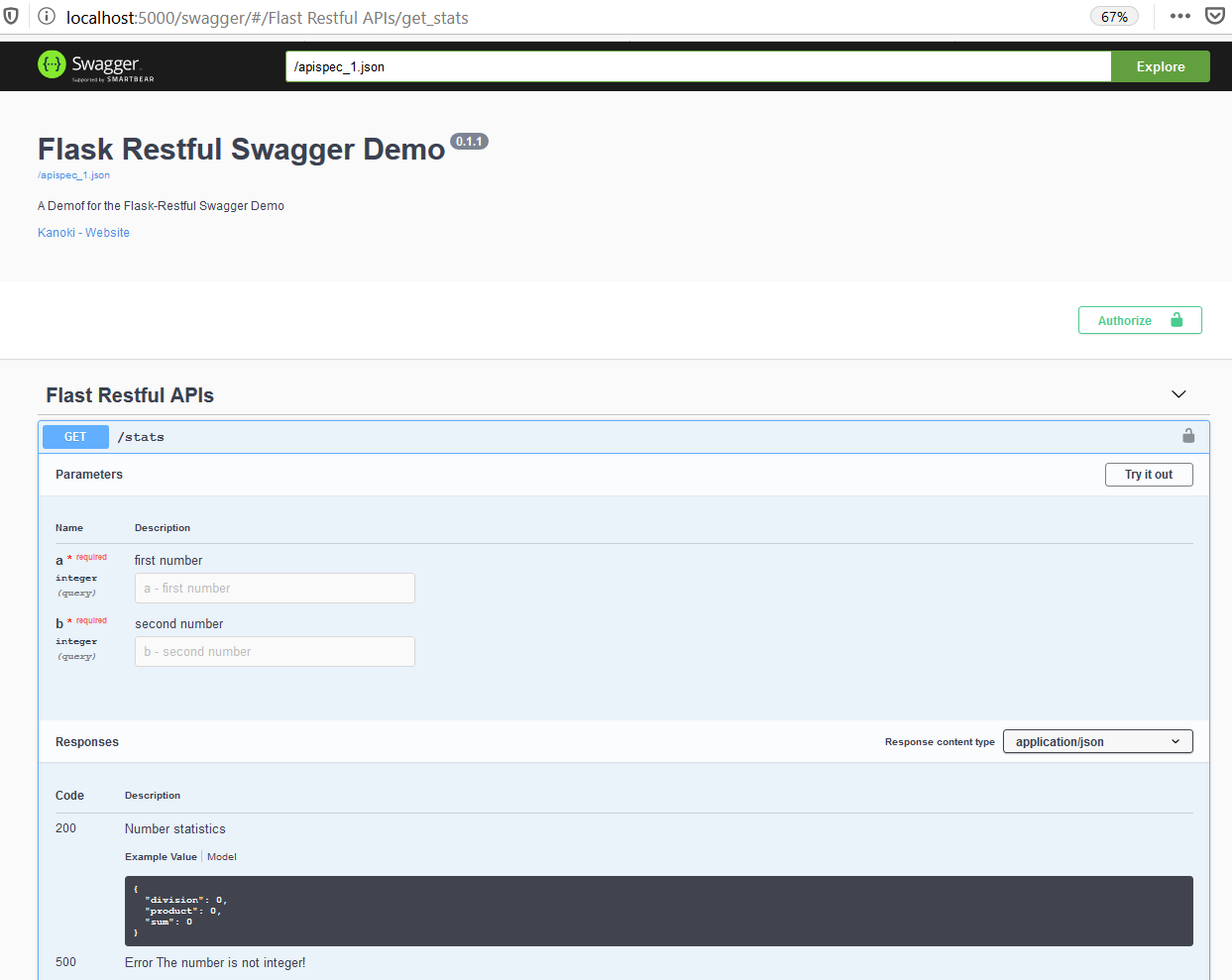
Now start the flask server and go to this link http://localhost:5000/apidocs/ which is a deafult swagger URL and you will see a swagger page
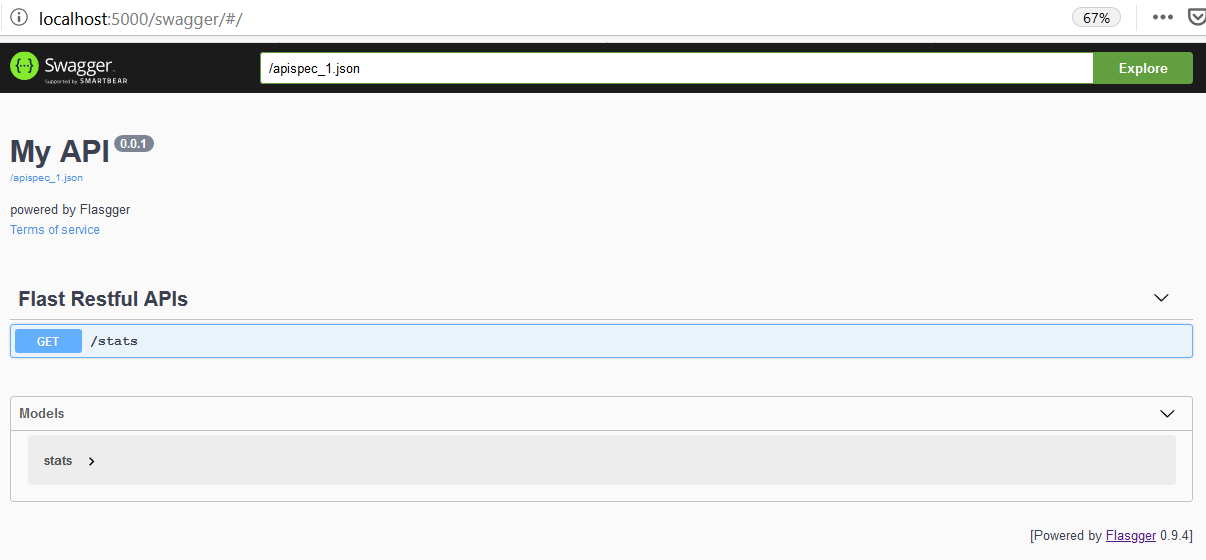
Templates and ConfigurationPermalink
Let’s make this more personalize by adding a swagger template and configurations.
We will use templates to give a description and title to our swagger page. In the configuration using spec_route you can change the URL where your swagger documentation should be published. So our new URL is http://localhost:5000/swagger/
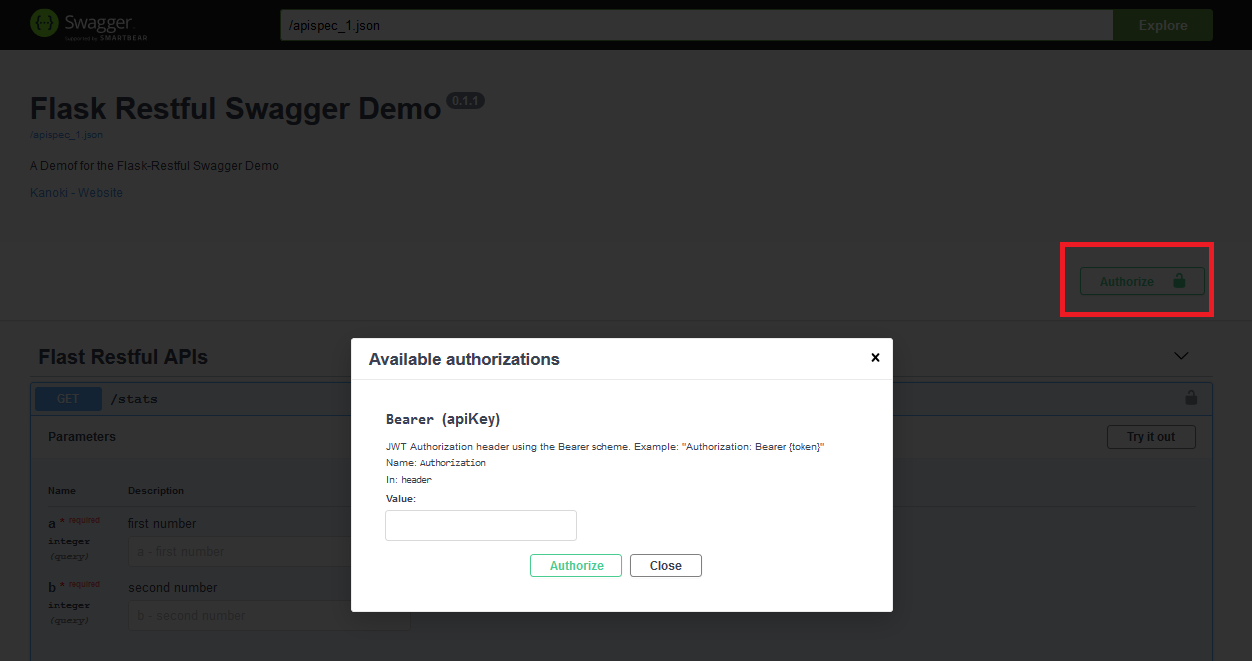
AuthorizationPermalink
We can also include the type of Authorization for API using Templates. Using securityDefinitions parameter we’ve included a bearer token Authorization to access the /stats API endpoint
import json,os
import logging
import sys
import config
import requests
from flask import Flask, request, Response, jsonify
from flask_restful import Api, Resource, reqparse
from flasgger import Swagger, swag_from
# Setup Flask Server
app = Flask(__name__)
# Create an APISpec
template = {
"swagger": "2.0",
"info": {
"title": "Flask Restful Swagger Demo",
"description": "A Demof for the Flask-Restful Swagger Demo",
"version": "0.1.1",
"contact": {
"name": "Kanoki",
"url": "https://Kanoki.org",
}
},
"securityDefinitions": {
"Bearer": {
"type": "apiKey",
"name": "Authorization",
"in": "header",
"description": "JWT Authorization header using the Bearer scheme. Example: \"Authorization: Bearer {token}\""
}
},
"security": [
{
"Bearer": [ ]
}
]
}
app.config['SWAGGER'] = {
'title': 'My API',
'uiversion': 3,
"specs_route": "/swagger/"
}
swagger = Swagger(app, template= template)
app.config.from_object(config.Config)
api = Api(app)
class Todo(Resource):
def get(self):
"""
post endpoint
---
tags:
- Flast Restful APIs
parameters:
- name: a
in: query
type: integer
required: true
description: first number
- name: b
in: query
type: integer
required: true
description: second number
responses:
500:
description: Error The number is not integer!
200:
description: Number statistics
schema:
id: stats
properties:
sum:
type: integer
description: The sum of number
product:
type: integer
description: The sum of number
division:
type: integer
description: The sum of number
"""
a = int(request.args.get("a"))
b = int(request.args.get("b"))
numsum = a+b
prod = a*b
div = a/b
return jsonify({
"sum": numsum,
"product": prod,
"division": div
})
## Api resource routing
api.add_resource(Todo, '/stats')
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(debug=True)
Now go to URL: http://localhost:5000/swagger/ and check your new and updated swagger page
Use External YAML files for specificationPermalink
So if you don’t want to use docstring as specification then flasgger let you store the specification in a YAML file too.
You need to configure flasgger to auto-parse the YAML file using @swag_from decorator to get specification from YAML or dict
Setting @swag_from’s validation parameter to True will validate incoming data automatically
Set a doc_dir in your app.config['SWAGGER'] and Swagger will load API docs by looking in doc_dir for YAML files stored by endpoint-name and method-name
import json,os
import logging
import sys
import config
import requests
from flask import Flask, request, Response, jsonify
from flask_restful import Api, Resource, reqparse
from flasgger import Swagger, swag_from
# Setup Flask Server
app = Flask(__name__)
# Create an APISpec
template = {
"swagger": "2.0",
"info": {
"title": "Flask Restful Swagger Demo",
"description": "A Demof for the Flask-Restful Swagger Demo",
"version": "0.1.1",
"contact": {
"name": "Kanoki",
"url": "https://Kanoki.org",
}
},
"securityDefinitions": {
"Bearer": {
"type": "apiKey",
"name": "Authorization",
"in": "header",
"description": "JWT Authorization header using the Bearer scheme. Example: \"Authorization: Bearer {token}\""
}
},
"security": [
{
"Bearer": [ ]
}
]
}
# swagger config
app.config['SWAGGER'] = {
'title': 'My API',
'uiversion': 3,
"specs_route": "/swagger/"
}
swagger = Swagger(app, template= template)
app.config.from_object(config.Config)
api = Api(app)
class Todo(Resource):
@swag_from("stats.yml", validation = True)
def get(self):
a = int(request.args.get("a"))
b = int(request.args.get("b"))
numsum = a+b
prod = a*b
div = a/b
return jsonify({
"sum": numsum,
"product": prod,
"division": div
})
## Api resource routing
api.add_resource(Todo, '/stats')
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(debug=True)
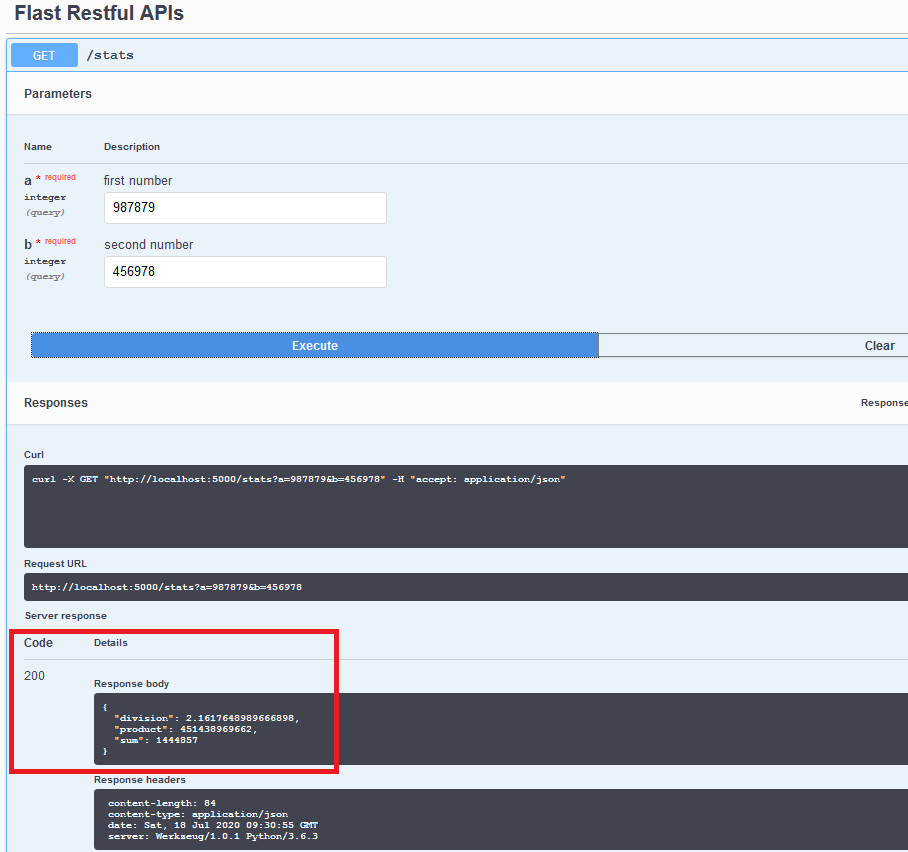
Try it out !!Permalink
Interact with your API and validate the Request and Response Model
ConclusionPermalink
I found flasgger an easy to use flask extension for quickly building your API documentation without much of hassle. This is compatible with Flask-RESTful and other REST frameworks too. You can easily deploy this inside a docker container just like any other python library and configure to customize it as per your need.
You can read more about how to build the specification and definitions for your Request and Response Models in the OPEN API documentation