Web Scraping Made Easy
Introduction
Web Scraping is an important and powerful way to extract the information from the Web and use it for further analysis to get insight from the data on the Web. Many websites publish their open web api’s to pull the data from their Websites but not everyone has api’s build to extract the data directly from the Website. Scraping the data from web can be a tedious task if you don’t have the right tools and knowledge. There are lot of steps that needs to be carried out after scrpaing the data from Web to make it further ready for analysis & investigations. There is an old saying that Data Scientists & Analysts spend 80% of their productive time in collecting and cleaning the data and only 20% of the time in analyzing and getting meaningful insight from it.
So Web Scraping is the process of getting the Unstructured data from the web and converting it into Structured format for further analysis. There are different set of tools available which can be used for scraping but before that we need to take a decision which tool will be best suited for our work. Before we go for the tool selection we need to have the requirements crystal clear for Scraping such as:
- How are the data stored in the website?
- Is my website AJAX powered?
- Do we have a secured site with logins
- What is the form of data that needs to captured
You should be legally Compliant before Scraping the data from any website. Read the Privacy Policy of the websites before you start the scraping
Python Scraping Libraries
- Beautifulsoup
- Mechanize
- Scrapy
- Urllib2/Requests
These are excellent libraries which extracts almost all kind of data from web but these tools are good for static websites So when you have to scrape websites where there is no Javascripts involved or static contents. However for Dynamic Websites where the pages are rendered using Javascript libraries like jquery cannot be scraped using these libraries.
Why Selenium Webdriver
Selenium is a tool which is primarily used for Browser Automation but can be used for web scraping as well if you have any requirement to fetch the data from dynamic websites or need to do some actions(like pressing a button or form submissions etc.) for the data to be populated on the page that cannot be achieved using these standard libraries. It can also be used to login to the webpages for the secured websites. Selenium can also help to scrap the data from websites where data has to be extracted from the multiple pages from paginations.
Now you might be wondering, Can Selenium fetch all the data that I need from HTML pages like tables, Div’s, Span texts etc. and the simple answer is Yes, it does scrape the entire webpage and dump it in the format of your choice, it has an upper hand with the above standard libraries because it wait for the page to loads and ensure the javascript is executed successfuly before it starts scraping the page.
Selenium identifies the elements using certain locators such as XPATH, CSSSELCTOR , ID, Name, link etc. The most efficient and common way to identify the element is using id and should always be the first choice when you have multiple choices to identify.
<div id=“article-20”>…..</div>
When you don’t have a choice to identify the elements if there are no id, name is present then the best option would be to go for either XPATH or CSS Selector, the best way to find the xpath for an element is do a right click on the element and select inspect and in the console right click and copy XPATH.
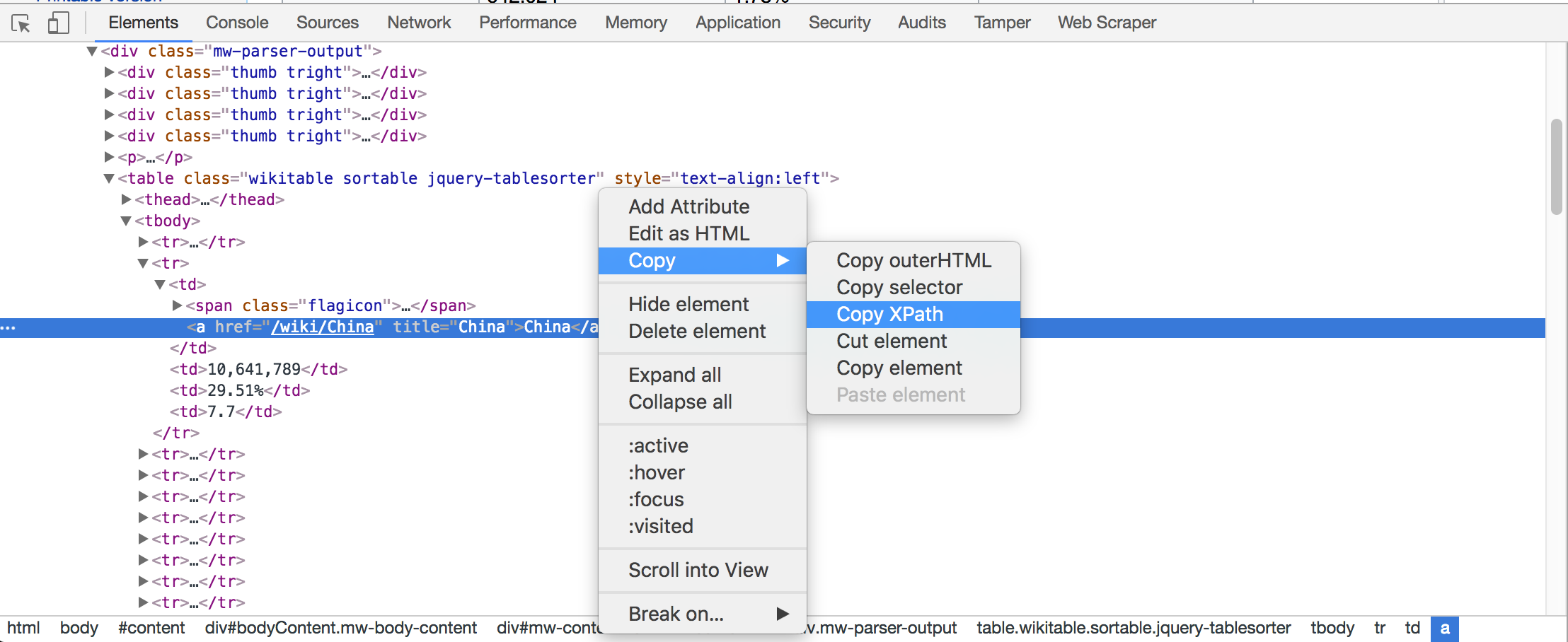
There are better ways for writing theXPATH, you can search the internet to find out how to writeXPATH efficiently. Here for this article we would use above method as a default way to find XPATH of the element, But if you know how to write XPATH any other way then feel free to use it.
Installing Selenium
Using pip install Selenium, it will install the latest version of the selenium on your system
pip install -U selenium
if you are using chrome as your default browser then chromedriver is required to run selenium on chrome, which is a server for implementing webdrivers wire protocol for chromium, because by default selenium only supports firefox browser but if you have to use any other browser of your choice then a supporting driver also needs to be downloaded and saved on the system. You can download the latest chromedriver from google website here
So now you have all the setups and chromedriver to get started.
Import Webdriver
First, Let’s import webdriver from selenium package and then instantiate the driver for chrome browser by providing the path where chromedriver file is saved
from selenium import webdriver import time import collections
Chromedriver path
chromedriver = “/Users/vbabu/WebScrap/src/com/proj/drivers/chromedriver”
Instantiate the driver object for Chrome
driver = webdriver.Chrome(chromedriver)
URL of the Website
url = ‘https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_countries_by_carbon_dioxide_emissions’
Learn how data is stored in HTML Tables
Now if you look at this wikipage it has a table with 4 columns. Let’s check the html data distribution for this table from where we need to extract the data. There is an HTML table structure and there are multiple rows and within each rows there are 4 columns, first column is Country, Second is CO2 emission, Third is Percent CO2 emission and Fourth is Emission per capita.
Let’s write the xpath for these column elements first. So right click on the first row and get the xpath from the console as shown above.
-
- Country: //*[@id=”mw-content-text”]/div/table/tbody/tr/td/a
-
- CO2 Emission: //*[@id=”mw-content-text”]/div/table/tbody/tr/td[2]
-
-
Percent CO2: //*[@id=”mw-content-text”]/div/table/tbody/tr/td[3]
- Emission per Capita : //*[@id=”mw-content-text”]/div/table/tbody/tr/td[4]
-
Find values
The values of each column can be extracted by using find_elements_by_xpath function which returns the list web elements and each of the web elements inside the list is equivalent to the column values in each row. And finally we need to extract the text inside each of these web elements using text function as shown in the final code block.
Extract the individual column values and store in a list as shown here:
List of values for country column
countrylst = driver.find_elements_by_xpath(‘//*[@id=”mw-content-text”]/div/table/tbody/tr/td/a’)
List of values for CO2 emission column
co2emitelst = driver.find_elements_by_xpath(‘//*[@id=”mw-content-text”]/div/table/tbody/tr/td[2]’)
List of values for Percent CO2 emission columns
percentco2lst = driver.find_elements_by_xpath(‘//*[@id=”mw-content-text”]/div/table/tbody/tr/td[3]’)
List of values Per capita CO2 emission columns
percapitalst = driver.find_elements_by_xpath(‘//*[@id=”mw-content-text”]/div/table/tbody/tr/td[4]’)
Data in Structured Format Now it’s time to get the values from these list and store them in a country dictionary, as shown here:
{ ‘South Korea’: { ‘CO2’: ‘642,024’, ‘PerCapita-CO2’: ‘23.4’, ‘Percent-CO2’: ‘1.78%’ }, ‘Malaysia’: { ‘CO2’: ‘279,174’, ‘PerCapita-CO2’: ‘11.9’, ‘Percent-CO2’: ‘0.77%’ } }
for cntryelem,co2emitelem,percntelem,percapitaelem in zip(countrylst,co2emitelst,percentco2lst,percapitalst): country[cntryelem.text]={} country[cntryelem.text][‘CO2’] = co2emitelem.text country[cntryelem.text][‘Percent-CO2’] = percntelem.text country[cntryelem.text][‘PerCapita-CO2’] = percapitaelem.text
Quit Driver
Finally you need to close the driver and terminates all the webdriver sessions
driver.quit()
Final Code