How to find distance between two Points based on Latitude and Longitude using Python and SQL
if you are working with GIS or POI data then you must be dealing with lat/long values and there would be use cases to calculate the distance between two points or places by evaluating the distance between their lat/long. There are so many apps out there which uses this information to show what are the restaurants, Medical Center, Shopping Malls within a specified radius from a particular location or what’s the distance between two places or What is the nearest walmart from the Wendy’s at Main Street. So there are hell lot of examples in our day to day life where we have to calculate the distance between two points and if you are working with any of the POI datasets as a Data Scientist then you might encounter such uses cases frequently.
if you are using Google Map API’s to calculate such distances then have you ever thought how google maps calculates the distance between two points. In the below image I’m trying to find the distance between the two points in Google maps. Look at that aerial distance(Black Bar Scale) that google displays for the distance between two points. This is not a road distance instead a shortest route between the two POI’s which is called as Crow Fly distance.
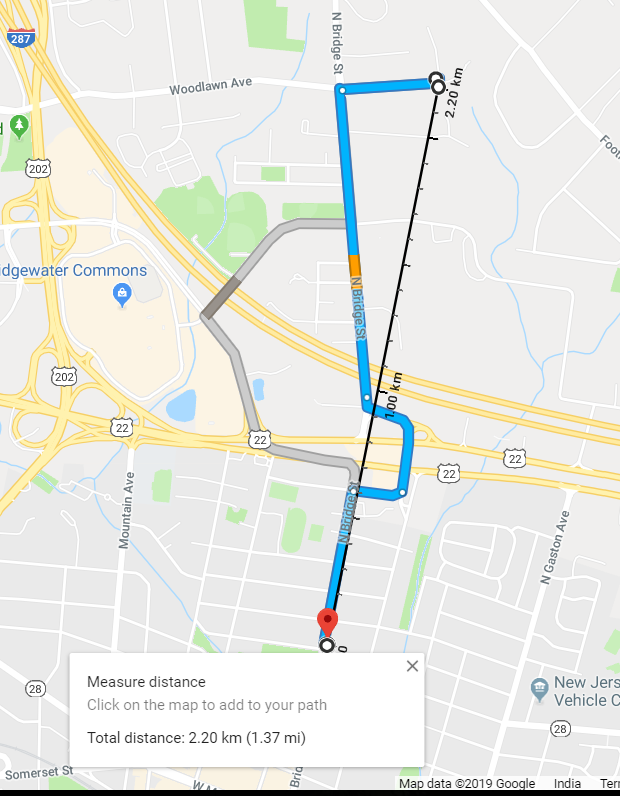
As per Wikipedia, the Geographical distance between two points/places is the distance measured along the surface of the earth. This distance between two lat/longs is based on some level of abstraction and it’s not an exact distance, which is unattainable if you are considering all the irregularities on the surface of earth.
Here are three abstractions which is considered for calculating the distance between two lat and longs:
a) Flat surface
The shortest distance between two points in a plain is a straight line and we can use Pythagoras Theorem to calculate the distance between two points.
b) Spherical surface
Greater Circle Distance Algorithms are used to calculate the distance between two points which assumes earth as a spherical object. Haversine Algorithm is used to calculate this distance.
c) Ellipsoidal surface
An ellipsoid approximates the surface of the earth much better than a sphere or a flat surface does. The shortest distance along the surface of an ellipsoid between two points on the surface is along the geodesic. Vincenty Algorithm is used to calculate this distance.
To calculate the distance between two points there are two popular algorithm Haversine and Geodesic distance is used:
Haversine computes the great circle distance on a sphere while Vincenty computes the shortest (geodesic) distance on the surface of an ellipsoid of revolution.
Let’s talk about the tool or methods used to calculate these distances. I am going to first show how to use MYSQL geospatial query libraries to calculate this distance and then we will see how to write code in Python for Haversine and Vincenty Formula to calculate the distance between two lat/longs using Geopy module.
Using MYSQL - st_distance_sphere
This returns the minimum spherical distance between two points or multipoints arguments on a sphere in metres. The points has to be entered within the following range:
latitude: [−90, 90] longitude: [−180, 180]
if you want the geodesic distance on the ellipsoid then you can use st_distance()
Spherical distance between Oklahoma City and Norman in Oklahoma
#long/Lat for Oklahoma City, OK
SET @g1 = Point(-97.520280,35.465438);
#long/Lat for Norman, OK
SET @g2 = Point(-97.441113,35.221090);
# Using Spherical Distance to calculate the distance between above two cities
SELECT st_distance_sphere(@g1,@g2)/1000
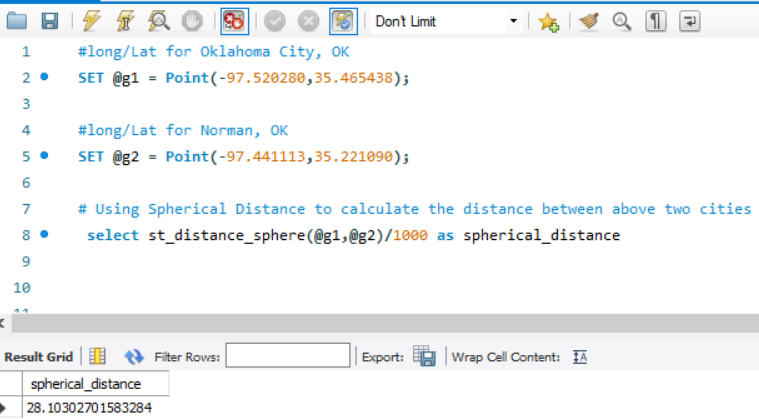
The Spherical distance between OKC and Norman is 28 Kms calculated using MYSQL st_distance_sphere formula. The st_distance_sphere gives the distance in metres and that’s the reason I have divided it by 1000 in the Select Query to get the result in KM.
Let’s see how Google Calculates the distance between these two cities:
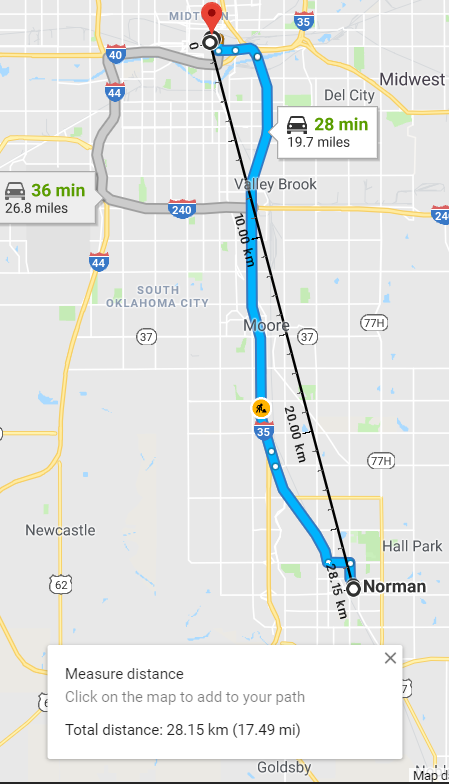
Google also calculates the same distance 28.15 Km as calculated by the MYSQL st_distance_sphere formula.
Using Pythagoras Theorem
The shortest distance between two points in plane is a straight line is calculated using the Pythagoras theorem and all of us have learnt this in our school and doesn’t need any introduction here
SELECT sqrt(power(35.465438-35.221090,2)+power(-97.441113-(-97.520280),2))*108 as Pythagoras_Distance
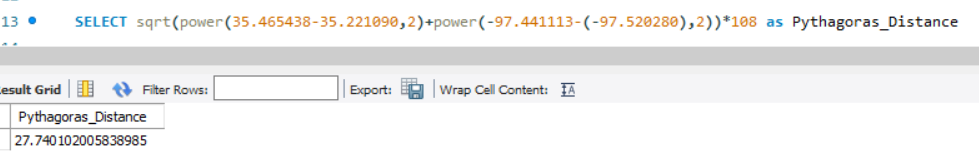
This method also calculates approximately the same distance as Spherical distance calculated using MYSQL and Google Maps. The calculated value is in Degress and to convert that to KM I have multiplied the result by 108 (i.e. radius of earth 6371*pi/180).
Using Python
Haversine Formula:
As per wikipedia,The haversine formula determines the great-circle distance between two points on a sphere given their longitudes and latitudes. Important in navigation, it is a special case of a more general formula in spherical trigonometry, the law of haversines, that relates the sides and angles of spherical triangles.
from math import radians, cos, sin, asin, sqrt
def haversine(lon1, lat1, lon2, lat2):
# convert decimal degrees to radians
lon1, lat1, lon2, lat2 = map(radians, [lon1, lat1, lon2, lat2])
# haversine formula
dlon = lon2 - lon1
dlat = lat2 - lat1
a = sin(dlat/2)**2 + cos(lat1) * cos(lat2) * sin(dlon/2)**2
c = 2 * asin(sqrt(a))
r = 6371 # Radius of earth in kilometers. Use 3956 for miles
return c * r
We will try to find distance between Oklahoma City and Norman in Oklahoma using the above Haversine Formula
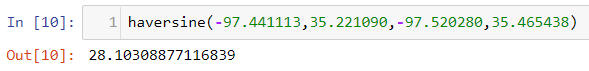
This distance is also same as the Google distance and the distance calculated by MYSQL.
Geodesic Distance Formula:
The geodesic distance is the shortest distance on the surface of an ellipsoidal model of the earth. The default algorithm uses the method is given by Karney (2013) (geodesic)
geopy.distance.distance currently uses geodesic.
from geopy import distance
okc_ok = (35.465438, -97.520280)
norman_ok = (35.221090, -97.4411131)
print(distance.distance(okc_ok , norman_ok ).km)
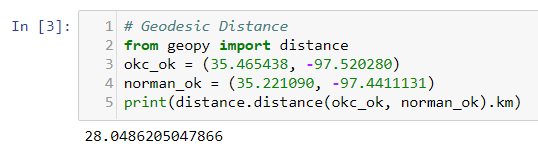
The Geodesic distance is also 28 KM which is same as the Spherical and Pythagoras distance that we calculated above. Since it’s a shorter distance so we don’t see much difference between each of these methods for distance calculation. if we take a longer distance like New York and Los Angeles then you would see some significant distance variation between each of these methods.
What Next?
Let’s Find Nearby Walmarts:
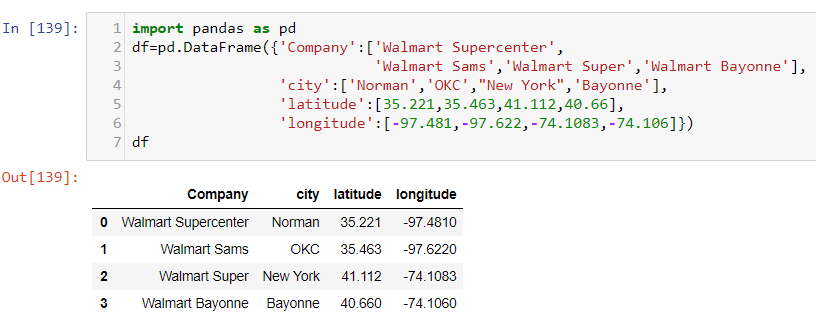
Let’s try out a simple exercise to find out the nearest walmart from the origin(i.e. Jersey City here) using haversine formula. For this task, I have taken 4 Walmarts Latitude and Longitudes in a Pandas dataframe as shown in the image below:
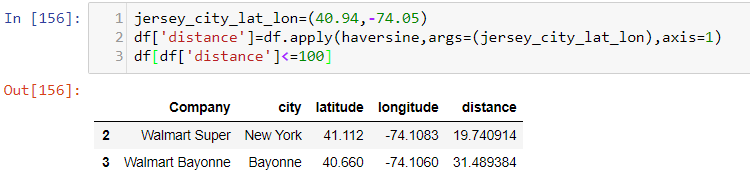
Now I want to find out all the Walmarts which is in a Radius of 50Km from the Jersey City. Using the Haversine formula explained above it returned two walmarts from the above dataframe, One Walmart is in New York and the other one is in Bayonne which is within the radius we are looking for since both New York and Bayonne lies within a radial distance of 50 Kms from Jersey City.
Conclusion:
We have seen how to calculate the distance between two points or Geo-Coordinates using MYSQL and Python. There are three different abstractions which are used for calculating these distance, Pythagoras theorem works fine for the smaller distance between two points and for more accurate solution geodesic distance is used using python’s geopy module and haversine formula or MYSQL st_distance_sphere is used for a spherical distance where we consider the earths plane as a sphere .